Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can occur for various reasons, impacting both men and women. Understanding the causes, available treatments, and preventive measures can help individuals manage and potentially reverse hair loss effectively.
Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It can occur for various reasons, impacting both men and women. Understanding the causes, available treatments, and preventive measures can help individuals manage and potentially reverse hair loss effectively.
Causes of Hair Loss
Hair loss can result from a multitude of factors, each contributing to the thinning or complete loss of hair. The most common causes include. Hereditary hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most prevalent cause. It affects both men and women and is characterized by a predictable pattern of hair thinning. In men, it usually starts with a receding hairline and balding on the crown, while women experience a general thinning across the scalp. Hormonal fluctuations due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or thyroid issues can lead to temporary or permanent hair loss. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) also contribute to hair thinning.
Certain medical conditions such as alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder, cause patchy hair loss. Scalp infections, like ringworm, and diseases such as lupus can also lead to hair loss. Hair loss can be a side effect of medications used for cancer, arthritis, depression, heart problems, and high blood pressure. Treatments like chemotherapy and radiation therapy also cause significant hair loss. Physical or emotional stress, poor diet, and lack of sleep can trigger hair shedding. Traction alopecia, caused by hairstyles that pull the hair tightly, and trichotillomania, a hair-pulling disorder, are also lifestyle-related causes.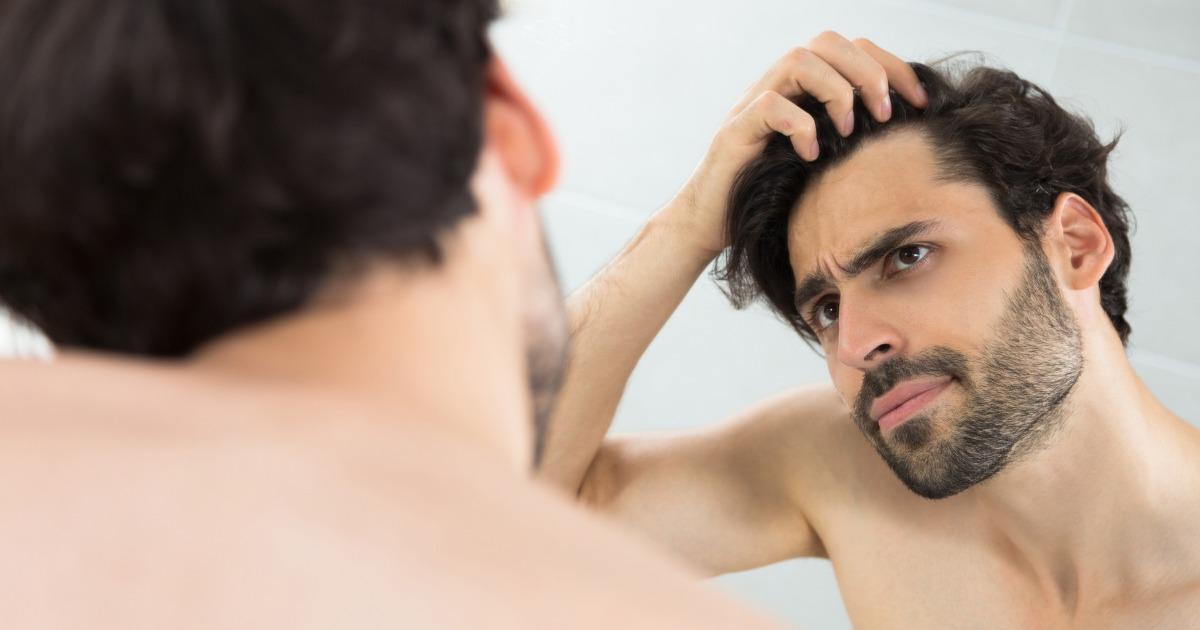 Treatments for Hair Loss
Treatments for Hair Loss
Treating hair loss involves addressing the underlying cause and exploring various medical and non-medical options. Over-the-counter and prescription medications can be effective. Minoxidil (Rogaine) is a topical treatment that stimulates hair growth and slows hair loss. Finasteride (Propecia) is an oral medication for men that reduces hair loss by blocking the hormone responsible for shrinking hair follicles.
This surgical procedure involves removing hair follicles from one part of the body (usually the back of the head) and transplanting them to thinning or balding areas. Techniques like Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) are commonly used. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) is a non-invasive treatment that uses red light to stimulate hair growth. It is believed to improve blood flow to the hair follicles, encouraging growth. PRP therapy involves injecting a concentration of the patient’s own platelets into the scalp to promote hair growth. Platelets contain growth factors that can stimulate hair follicles.
Some people opt for natural remedies such as essential oils (like rosemary and peppermint), dietary supplements (like biotin and iron), and scalp massages to improve circulation and promote hair growth.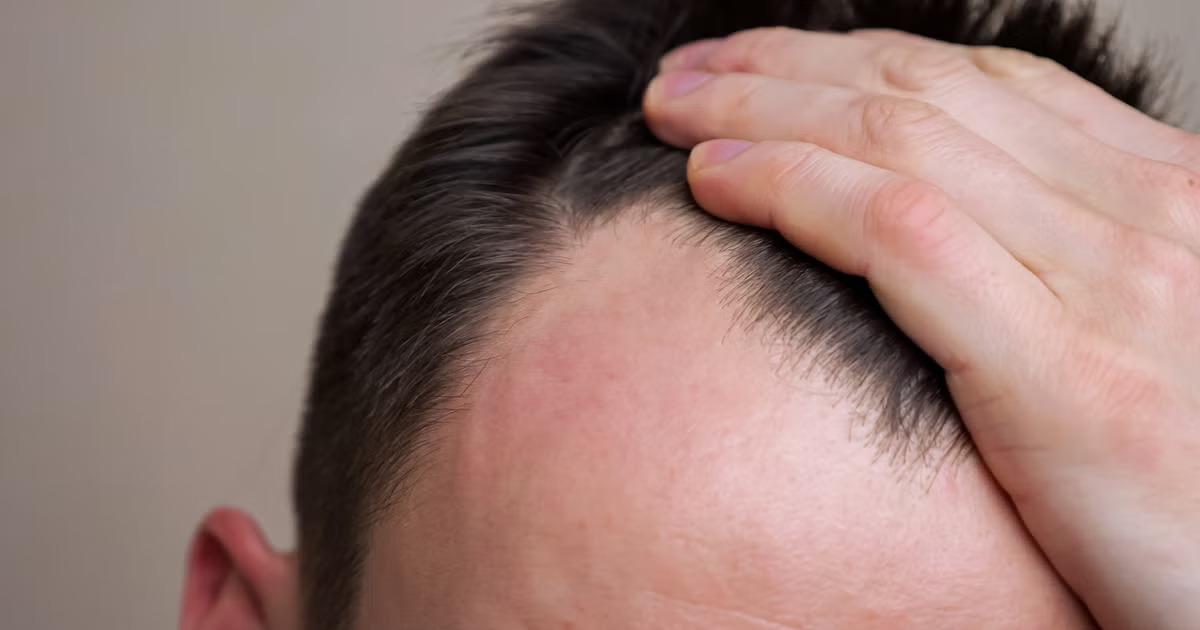 Prevention of Hair Loss
Prevention of Hair Loss
Preventing hair loss involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits and taking proactive measures
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports hair health. Foods high in protein, iron, and vitamins A and C are particularly beneficial. Avoiding excessive styling, harsh treatments, and tight hairstyles can prevent traction alopecia. Using gentle shampoos and conditioners and minimizing heat exposure from blow dryers and styling tools also helps. Reducing stress through exercise, meditation, and relaxation techniques can prevent stress-induced hair loss. Ensuring adequate sleep and maintaining a healthy work-life balance are crucial.
Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help detect and address underlying health issues that may cause hair loss. Early intervention is key to managing hair loss effectively.
